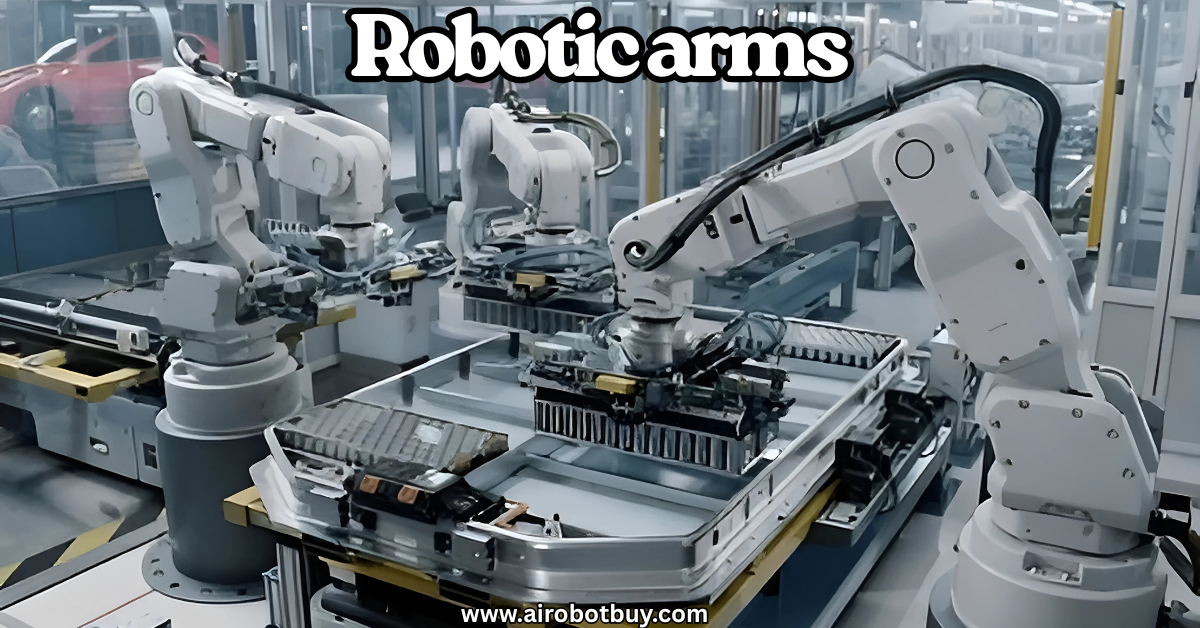
Robotic automation in manufacturing is redefining how modern factories operate. Across industries, manufacturers are adopting advanced robotics to enhance product quality, boost productivity, and reduce labor costs. By integrating robotic systems with conveyance, vision, and other automated technologies, production lines are becoming faster, smarter, and more precise. This transformation not only improves operational efficiency but also drives innovation and competitiveness in today’s global manufacturing landscape.
Robotic Automation in Manufacturing – Complete guide 2025-2026
What Is Manufacturing Automation?
Manufacturing automation refers to the use of advanced technologies—such as robotics, vision systems, and intelligent software—to streamline and optimize production processes. Through robotic automation in manufacturing, companies can minimize human error, speed up production, and maintain consistent product quality.
Automation can appear in many forms, from autonomous robots that handle materials and products in specific stages of production to artificial intelligence systems that detect defects with high-speed cameras. Today, most manufacturing companies invest in at least one type of automation—whether it’s a single robotic arm or a fully automated production line—to improve efficiency, reduce labor costs, and stay competitive in a rapidly evolving industry.
Robotics in Manufacturing Industry
When discussing automation, robotic systems often take center stage. In modern factories, robotic automation in manufacturing involves the use of machines and robotic arms to perform tasks that were once completed manually. These robots, such as three- or six-axis robotic arms—handle material movement, pick-and-place operations, and repetitive production tasks with unmatched speed and precision.

By integrating robotics into high-volume or repetitive processes, manufacturers can ensure consistency, increase throughput, and minimize downtime. Controls engineers can program these robots to perform identical actions every cycle or adapt them with advanced sensors for flexible manufacturing needs.
However, not every production line requires robotics in every stage. Before implementing robotic automation, manufacturers must clearly define their challenges and goals. Partnering with an experienced robotics integrator helps ensure that each automated solution genuinely enhances efficiency, uptime, and product quality, rather than overcomplicating the workflow.
Benefits of Robotic Automation in Manufacturing
The adoption of robotic automation in manufacturing brings a wide range of benefits that improve both production performance and overall business operations. From enhanced quality to long-term cost savings, robotics and manufacturing are a natural fit for efficiency-driven industries.
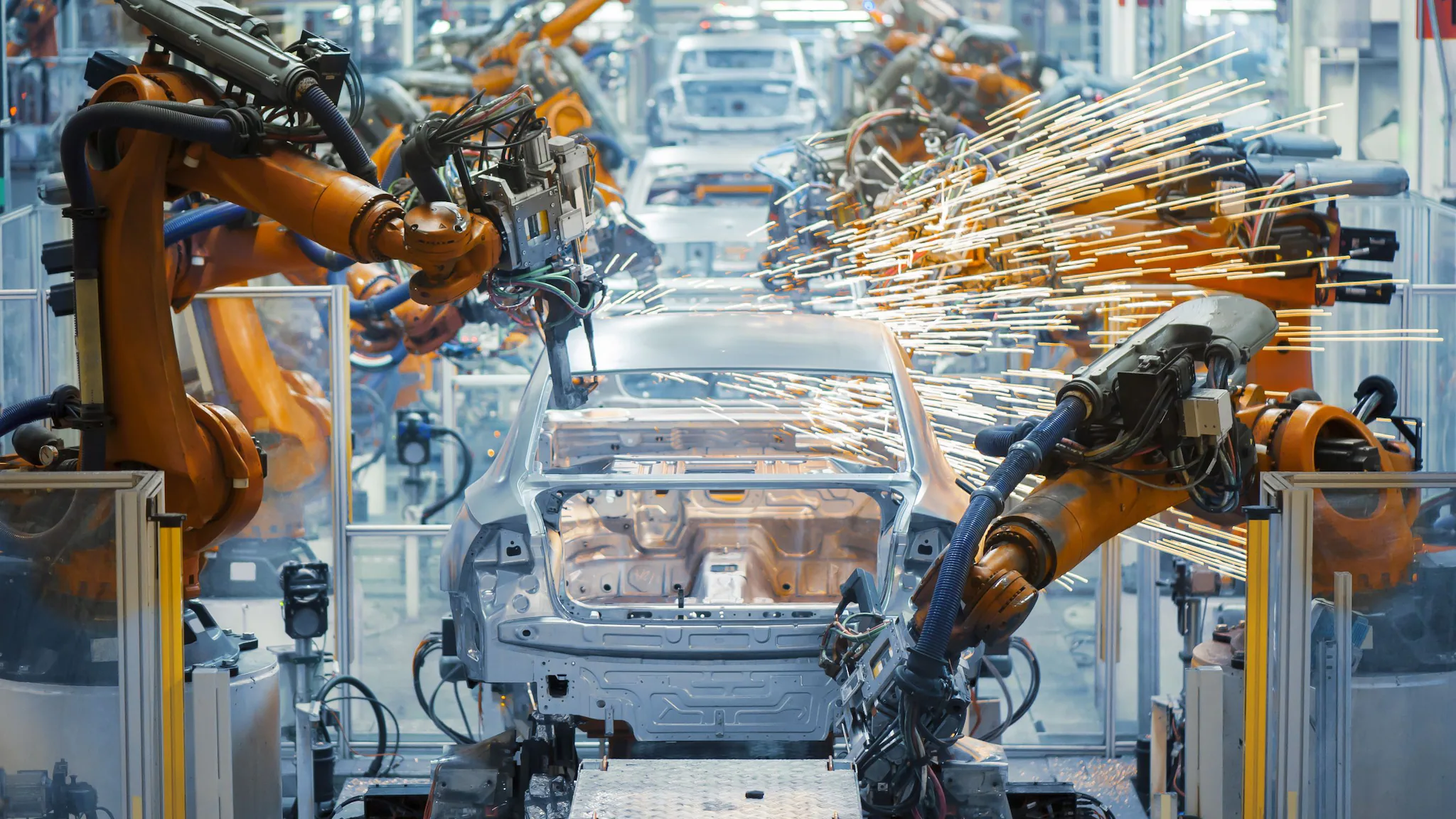

1. Increased Productivity and Efficiency
Robots dramatically increase productivity by performing complex or repetitive tasks faster and more accurately than human workers. With robotic automation, manufacturers can achieve consistent output levels around the clock since robots operate continuously without fatigue. This improved efficiency enables companies to meet growing market demands more effectively and maintain a competitive edge.
2. Enhanced Quality and Precision
Consistency and precision are crucial in manufacturing—and that’s where robots excel. By following programmed instructions with exact accuracy, robotic systems ensure every product meets the same high standards. This reliability minimizes defects, reduces waste, and enhances customer satisfaction through consistently high-quality output.
3. Improved Workplace Safety
Robotic automation in manufacturing greatly enhances workplace safety by taking over hazardous, repetitive, or physically demanding tasks. Robots can handle dangerous materials, operate in extreme environments, and perform heavy lifting, reducing injury risks for human workers. A safer workplace also leads to fewer compensation claims and better employee morale.
4. Long-Term Cost Savings
Although the initial investment in robotics can be significant, the long-term return on investment is substantial. Increased efficiency, reduced waste, fewer errors, and improved safety all contribute to significant cost savings. Robots also lower operational expenses by minimizing downtime and rework, ensuring smooth and reliable production cycles.
5. Scalability and Flexibility
Robotic systems are highly scalable, allowing manufacturers to quickly adjust production capacity to meet shifting market demands. Whether increasing output during peak seasons or scaling down during slower periods, robotic automation offers flexibility that traditional processes simply cannot match.
While the benefits of robotic automation in manufacturing are clear, it’s important to also recognize the challenges that come with implementation—such as upfront costs, maintenance requirements, and workforce adaptation. These considerations must be managed carefully to ensure a smooth transition to automation.
Types of Robots Used in Manufacturing
In the world of robotic automation in manufacturing, different types of robots perform specialized functions to optimize efficiency, precision, and productivity. These machines are the backbone of modern factories, streamlining workflows, ensuring consistent quality, and minimizing downtime across various production processes.

Industrial Robots
Industrial robots are the foundation of automated manufacturing systems. Known for their strength, speed, and precision, these robots perform a wide range of repetitive and labor-intensive tasks—such as welding, painting, assembly, and material handling—with exceptional accuracy. Their ability to operate 24/7 without fatigue helps manufacturers maintain consistent output and meet growing production demands.
Below are the most common types of industrial robots used in robotic automation today:
-
Articulated Robots:
Equipped with rotary joints that mimic the movement of a human arm, articulated robots are highly flexible and adaptable. They excel in tasks that require a wide range of motion, such as welding, packaging, and assembly. -
SCARA Robots (Selective Compliance Assembly Robot Arm):
Designed for high-speed and high-precision lateral movements, SCARA robots are ideal for pick-and-place operations, small part assembly, and other repetitive processes that demand accuracy and speed. -
Delta Robots:
Recognized for their lightweight structure and lightning-fast movements, delta robots are perfect for operations that require rapid and precise positioning, such as packaging, sorting, and electronic component assembly. -
Cartesian Robots (Gantry Robots):
Operating along three linear axes (X, Y, and Z), Cartesian robots provide straightforward control and exceptional precision. They are widely used in CNC machining, 3D printing, and automated inspection systems where linear motion and accuracy are critical.
Each type of industrial robot brings unique advantages to robotic automation in manufacturing, enabling businesses to select the right technology for their specific operational goals and production requirements.
Challenges and Considerations in Robotic Automation Integration
While robotic automation in manufacturing delivers impressive benefits, integrating these advanced systems into existing production environments presents several key challenges. Understanding and addressing these considerations ensures smoother implementation and maximum ROI.
1. High Initial Investment
The upfront cost of adopting industrial robots can be significant, especially for small and mid-sized manufacturers. Expenses include purchasing robotic units, installing supporting infrastructure, and training staff. Conducting a thorough cost-benefit analysis and estimating long-term returns are essential steps before committing to automation. Over time, however, increased efficiency and reduced operational costs often offset the initial investment.
2. Workforce and Job Displacement Concerns
Automation often raises concerns about job loss as robots replace repetitive, labor-intensive tasks. However, robotic automation in manufacturing also creates new opportunities for human workers—especially in areas such as programming, maintenance, and system optimization. By reskilling and upskilling employees, manufacturers can transform their workforce to align with the evolving demands of Industry 4.0.
READ ALSO: Industrial Robotics Future Trends Every Business Should Know
3. Technical Integration and Maintenance
Integrating robotic systems with existing manufacturing equipment and software can be technically complex. Ensuring seamless communication between robots, conveyors, sensors, and control systems is crucial to prevent downtime. Regular maintenance, software updates, and real-time monitoring are also necessary to maintain peak performance and reduce operational risks.
4. Regulatory and Compliance Challenges
Manufacturers must navigate a wide range of safety and compliance regulations when deploying robotic systems. Adhering to occupational safety standards, electrical codes, and data protection regulations is vital to maintaining operational integrity. Staying up to date with evolving robotics laws and standards helps companies avoid compliance issues and ensures safe operation.
5. Customization and Scalability
Every production line is unique, meaning robotic systems must often be customized to meet specific manufacturing needs. Planning for scalability is equally important—robotic automation should be adaptable enough to handle future production growth or changes in product design. This flexibility ensures long-term value and sustainability in a rapidly advancing industrial landscape.
By carefully addressing these challenges, manufacturers can integrate robotic automation in manufacturing successfully, unlocking higher productivity, better quality, and a strong competitive advantage in today’s dynamic market.
The Future of Robotic Automation in Manufacturing
The future of robotic automation in manufacturing is defined by innovation, intelligence, and sustainability. As technology continues to evolve, robotics will play an even greater role in transforming production lines into smarter, greener, and more collaborative environments.

1. AI, Machine Learning, and Smart Robotics
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) with robotic systems marks a revolutionary shift in the manufacturing landscape. These technologies enable robots to learn, adapt, and self-optimize over time, leading to enhanced precision, speed, and flexibility.
Through AI-driven automation, robots can detect errors, predict maintenance needs, and make data-based adjustments without human intervention. Companies like TDK are advancing this trend by developing intelligent sensors and components that enhance robotic perception and decision-making capabilities.
2. Eco-Friendly and Sustainable Manufacturing
Sustainability is now a major priority for the industrial sector, and robotic automation in manufacturing plays a vital role in achieving it. Automated systems help reduce material waste, optimize energy usage, and ensure efficient resource management. By promoting energy-efficient operations and precision-driven processes, robotics supports eco-friendly manufacturing practices and aligns production with global sustainability goals.
3. Human-Robot Collaboration and Usability
The next generation of manufacturing focuses on collaborative robotics (cobots), robots designed to safely and efficiently work alongside humans. Enhancing human-robot interaction through intuitive interfaces and improved usability allows workers to guide, teach, and collaborate with robots seamlessly. This synergy not only boosts productivity but also creates safer, more dynamic, and engaging workplaces.
4. Shaping the Global Manufacturing Landscape
As robotic automation becomes more advanced, affordable, and accessible, its influence on global manufacturing industries will continue to grow. From small-scale factories to large industrial facilities, robots are setting new benchmarks for precision, quality, and efficiency. This ongoing transformation is fueling economic growth, creating new technical roles, and redefining the future of industrial production worldwide.
Robotic automation in manufacturing has become the cornerstone of modern industry, transforming how products are designed, assembled, and delivered. From improving productivity and precision to enhancing workplace safety and sustainability, robotics continues to redefine efficiency at every level of production.
As technology evolves, the integration of artificial intelligence, machine learning, and collaborative robotics will make factories even smarter, more adaptable, and environmentally responsible. While challenges such as high initial costs and technical integration exist, the long-term rewards, greater output, consistent quality, and reduced downtime, far outweigh the hurdles.
Ultimately, embracing robotic automation in manufacturing is not just about keeping up with innovation; it’s about shaping the future of industry itself. Manufacturers that invest in intelligent, automated solutions today are building the foundation for a faster, safer, and more sustainable tomorrow